| ☰ See All Chapters |
Checked exceptions vs. Unchecked Exceptions in Java
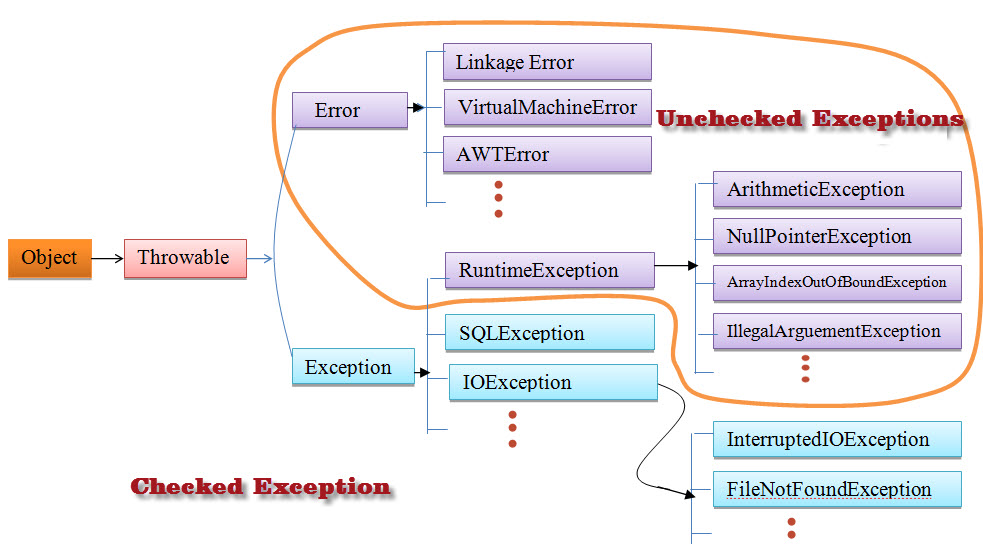
| Checked exceptions | Unchecked exceptions |
Definition | Any exception which is must to handle or catch it while writing the program is called checked exception. | Any exception which is not mandatory to handle or catch it while writing the program or executing the program is called unchecked exception. |
Example | FileNotFoundException FileReader file = new FileReader("file.txt");
IOException InputStream input = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
| NullPointerException Employee e1 = null; System.out.println(e.name); ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException int a[] = new int[10]; System.out.println(a[20]); |
Hierarchy | They are all subclasses of Exception. | They are all subclasses of RuntimeException. |
Ignorance | Must be formally acknowledged in the program one way or another. | Unchecked exceptions can be ignored completely in the code if desired. |
Compilation | If your code fails to either handle a checked exception or declare that it is thrown, your code won't compile. | If your code fails to either handle an Unchecked exception or declare that it is thrown, your code will compile. |
Handling verification | Checked Exception in Java is those Exceptions whose handling is verified during Compile time. | Unchecked Exception in Java is those Exceptions whose handling is not verified during Compile time. |
JVM | JVM enforces developer to handle or catch it: | JVM does not enforce developer to handle or catch it: |
Propagation | By default Unchecked Exceptions are forwarded in calling chain (propagated). | By default, Checked Exceptions are not forwarded in calling chain (propagated). |
Caught/ uncaught | They are also called as caught exceptions | They are also called as uncaught exceptions. |
Throws clause | The throws clause on a method header must be included for checked exceptions that are not caught and handled in the method. | The throws clause on a method header is not mandatory to be included for unchecked exceptions that are not caught and handled in the method. |
Scenario | CheckedException represent scenario with higher failure rate | UnCheckedException are mostly programming mistakes. |
Overriding |
If the superclass method does not declare any exception, subclass overridden method cannot declare the checked exception but it can declare unchecked exception.
If the superclass method declares an exception, subclass overridden method can declare same, subclass exception or no exception but cannot declare parent exception. | |
Use |
|
|
Checked exceptions cannot be foreseen by the programmer. But it is the duty of programmer to think from all dimensions about different possibilities that may occur.
All Chapters

